Explain the participants in foreign exchange market - Explain the participants in the foreign exchange market and their roles in facilitating currency exchange. From commercial banks to central banks, corporations, hedge funds, and retail investors, each participant plays a unique part in shaping the global currency market.
This article delves into the activities of these participants, exploring how they interact, influence exchange rates, and contribute to the overall functioning of the foreign exchange market.
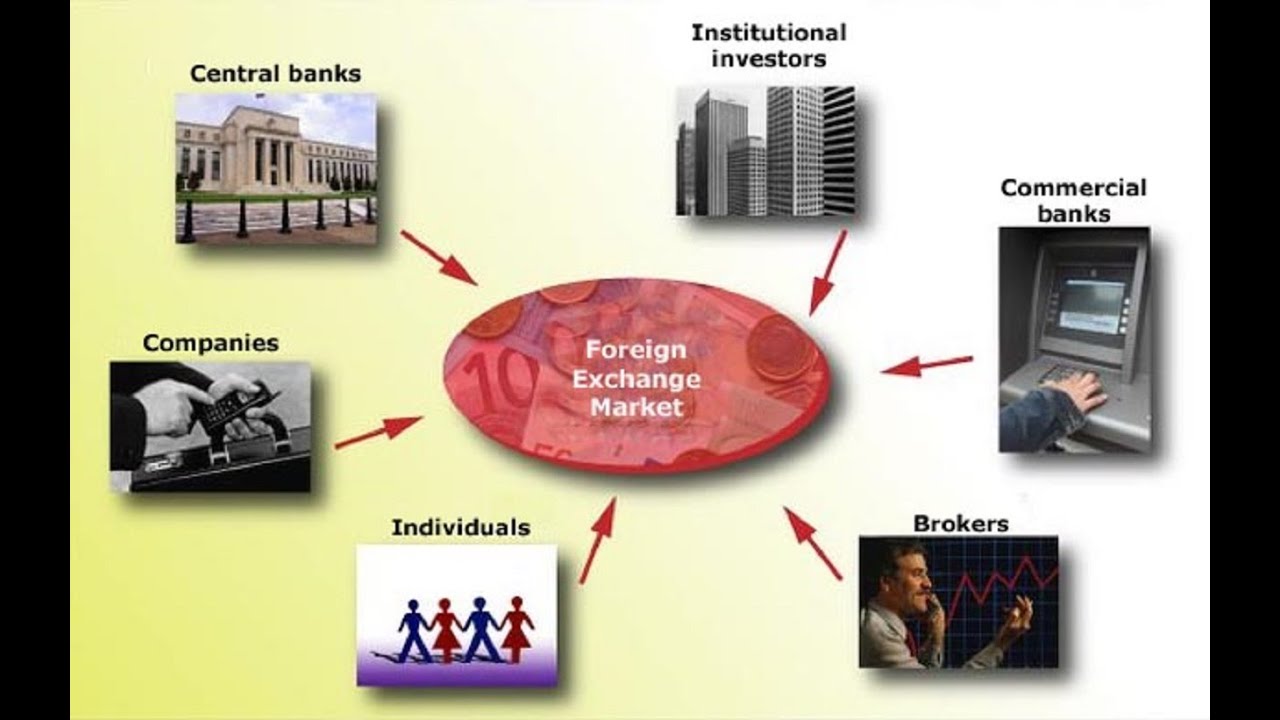
Participants in Foreign Exchange Market
Commercial Banks
Commercial banks are the most active participants in the foreign exchange market. They facilitate foreign exchange transactions for their customers, including individuals, businesses, and other financial institutions. Commercial banks also trade foreign currencies on their own account to manage their risk and profit from currency fluctuations.
Central Banks
Central banks are responsible for managing the monetary policy of their respective countries. They participate in the foreign exchange market to influence the value of their currencies and to manage their foreign exchange reserves. Central banks may also intervene in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the currency or to support their economic policies.
Discover how jelaskan fungsi dari foreign exchange market has transformed methods in RELATED FIELD.
Other Participants
Other participants in the foreign exchange market include corporations, hedge funds, and retail investors. Corporations may need to exchange currencies to conduct international business, while hedge funds and retail investors may trade currencies to speculate on their value.
Discover the crucial elements that make foreign exchange market haram or halal the top choice.
Types of Foreign Exchange Transactions

Foreign exchange transactions involve the exchange of currencies between different countries. These transactions can be classified into various types based on their purpose, timing, and complexity. The primary types of foreign exchange transactions include spot transactions, forward transactions, and swaps.
Spot Transactions
Spot transactions are the most common type of foreign exchange transaction. They involve the immediate exchange of currencies at the prevailing market rate. The settlement of spot transactions typically occurs within two business days. Spot transactions are used for various purposes, such as settling international trade payments, hedging against currency fluctuations, and speculating on currency movements.
Check foreign exchange market leader to inspect complete evaluations and testimonials from users.
Forward Transactions
Forward transactions are contracts to exchange currencies at a specified future date and rate. They are used to lock in an exchange rate for a future transaction, reducing the risk of currency fluctuations. Forward transactions are commonly used by businesses that engage in international trade and need to manage their foreign exchange exposure.
Swaps
Swaps are complex financial instruments that involve the exchange of currencies and interest rates over a specified period. They are used for various purposes, such as hedging against interest rate risk, managing currency exposure, and speculating on currency movements. Swaps are typically used by large financial institutions and sophisticated investors.
Factors Affecting Foreign Exchange Rates
Foreign exchange rates are constantly fluctuating due to a complex interplay of economic and political factors. These factors can influence the demand and supply of currencies, leading to changes in their relative values.Economic Factors
* Interest rates: Higher interest rates make a currency more attractive to investors, increasing demand and raising its value. * Inflation: High inflation erodes the purchasing power of a currency, reducing its demand and lowering its value. * Economic growth: A growing economy attracts investment and increases demand for its currency. * Trade balance: A positive trade balance (exports exceed imports) increases demand for a currency, while a negative balance decreases it. * Government debt: High government debt can raise concerns about the country's financial stability, reducing demand for its currency.Political Factors
* Political stability: Political instability and uncertainty can make investors wary of investing in a country, reducing demand for its currency. * Government policies: Changes in government policies, such as tax laws or trade agreements, can impact the attractiveness of a currency. * International relations: Diplomatic tensions or conflicts can affect the value of currencies involved. * Natural disasters: Major natural disasters can disrupt economic activity and affect the demand for a currency.Examples of Events Impacting Foreign Exchange Rates
* The 2008 financial crisis led to a sharp decline in the value of the US dollar due to concerns about the country's economic health. * The Brexit referendum in 2016 caused a drop in the value of the British pound due to uncertainty about the country's future economic relationship with the EU. * The COVID-19 pandemic led to a surge in demand for the US dollar as investors sought safe-haven assets.Regulation of the Foreign Exchange Market: Explain The Participants In Foreign Exchange Market
The foreign exchange market is a global, decentralized market for the trading of currencies. It is the largest financial market in the world, with a daily trading volume of over $5 trillion. Due to its size and complexity, the foreign exchange market is subject to a variety of regulations by governments and international organizations.
Role of Government
Governments play a significant role in regulating the foreign exchange market. They do this by:
- Setting interest rates
- Imposing capital controls
- Intervening in the foreign exchange market
Role of International Organizations
International organizations also play a role in regulating the foreign exchange market. The most important of these organizations is the Bank for International Settlements (BIS). The BIS is a central bank for central banks. It provides financial services to central banks and promotes cooperation among them.
Types of Regulations, Explain the participants in foreign exchange market
There are a variety of different types of regulations that are in place to regulate the foreign exchange market. These regulations include:
- Capital controls
- Exchange rate pegs
- Margin requirements
- Anti-money laundering regulations
Benefits of Regulation
There are a number of benefits to regulating the foreign exchange market. These benefits include:
- Promoting stability in the foreign exchange market
- Preventing excessive volatility in exchange rates
- Protecting investors from fraud and abuse
Challenges of Regulation
There are also a number of challenges to regulating the foreign exchange market. These challenges include:
- The global nature of the foreign exchange market
- The difficulty of enforcing regulations
- The potential for unintended consequences
Wrap-Up

In conclusion, the foreign exchange market is a complex and dynamic arena where various participants interact to facilitate currency exchange. Understanding their roles and activities provides valuable insights into the factors that drive exchange rates and shape the global economy.
